Introduction
Sign up, sign in, and Log out are three things that we always have in mind while developing a web application. The following points will be discussed in depth as part of this.
- How can I sign up or register a new user in our app?
- Built the User Login Page
- How to use the built-in Authorize Attribute
- Adding the logout functionality
- How to utilize Forms Authentication in an MVC application to accomplish all of the above goals?
The following three steps are required to implement Forms Authentication in an MVC application.
- In the web.config file, set the authentication mode to Forms.
- FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie is required to use for login.
- Again FormAuthentication.SignOut is required to use for logout.
Open any version of your SQL Server database and it makes no difference which version you have.
Create Employee Table
Create Department Table
Create Users Table
Create Users Table
Create UserRoles Table
Step 2
Make a new project with Visual Studio 2019 or another editor of your choice.
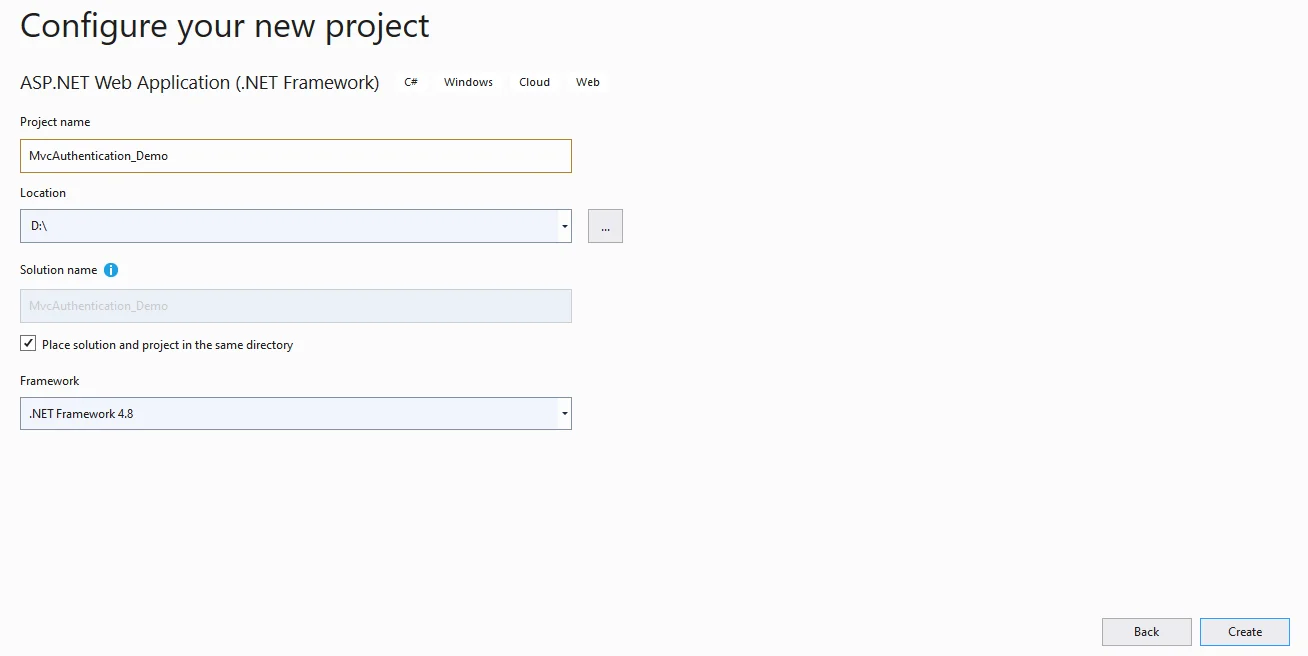
Step 3
Choose the "ASP.NET web application" project and give an appropriate name to your project and then click on "Create".
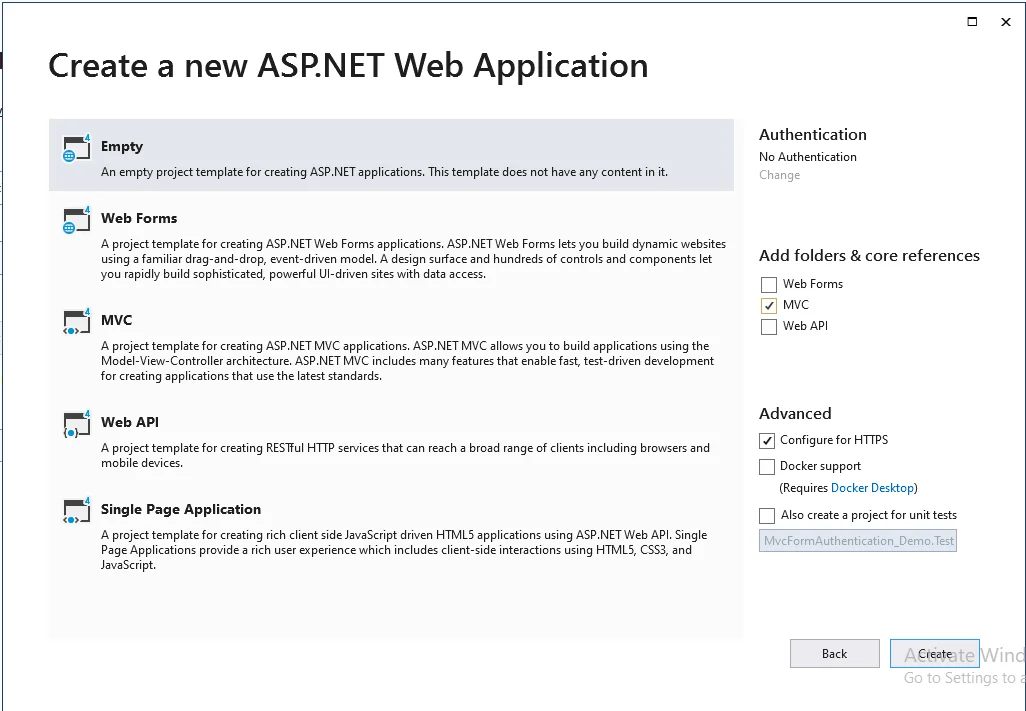
Step 4
Then, choose “Empty” and select MVC from the checkbox and then add the project.
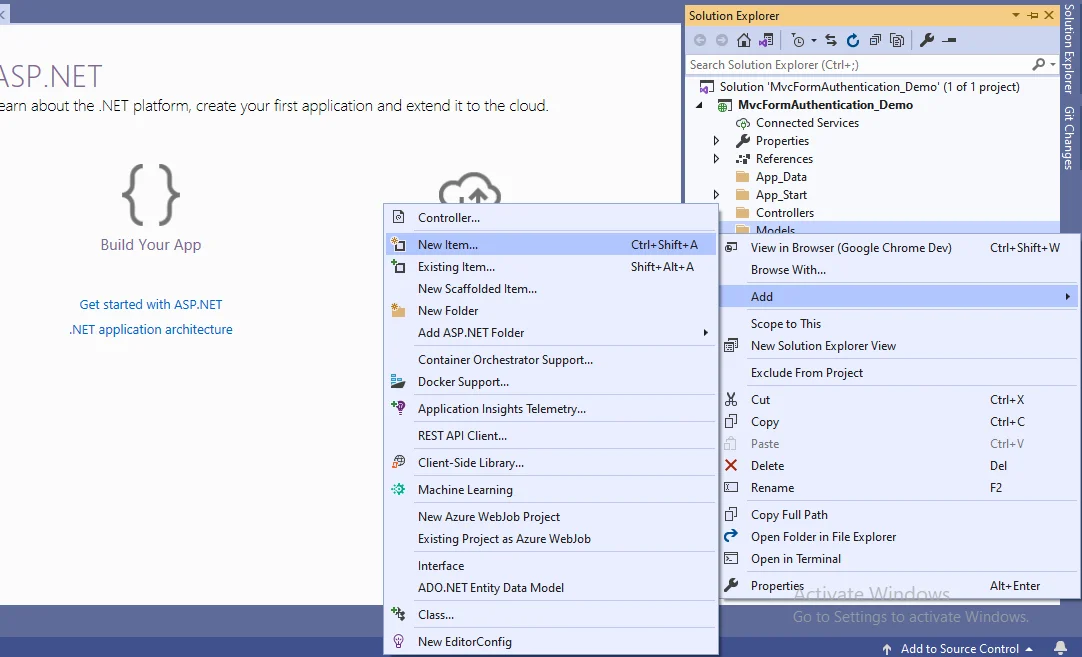
Step 5
Add a database model by right-clicking the Models folder. Now, add the Entity Framework and for that, you have to right-click on the Models folder and then choose "New item…".
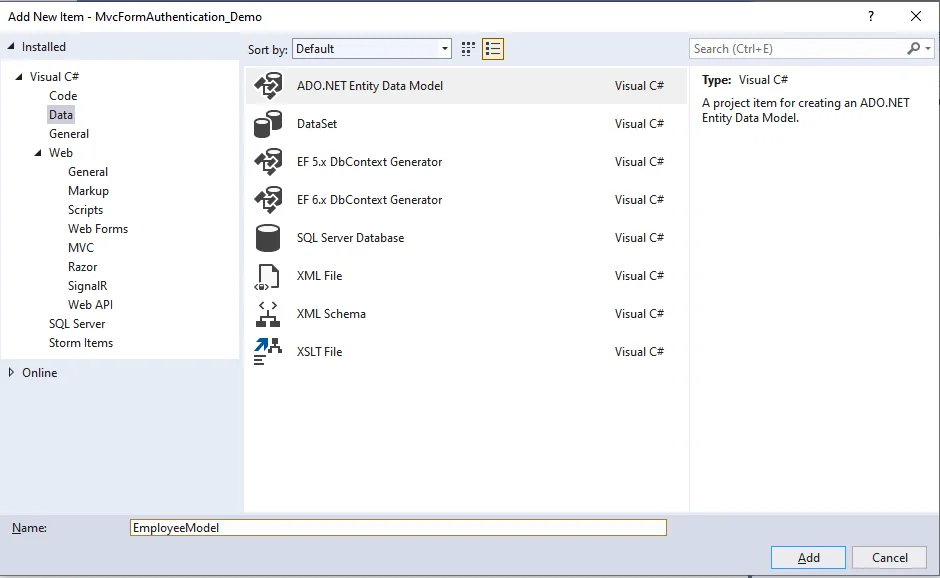
You will be presented with a window; from there, pick Data from the left panel and select ADO.NET Entity Data Model, name it EmployeeModel (this name is not required; any name will suffice), and click "Add."
The wizard will open after you click "Add a window." Click "Next" after selecting EF Designer from the database.
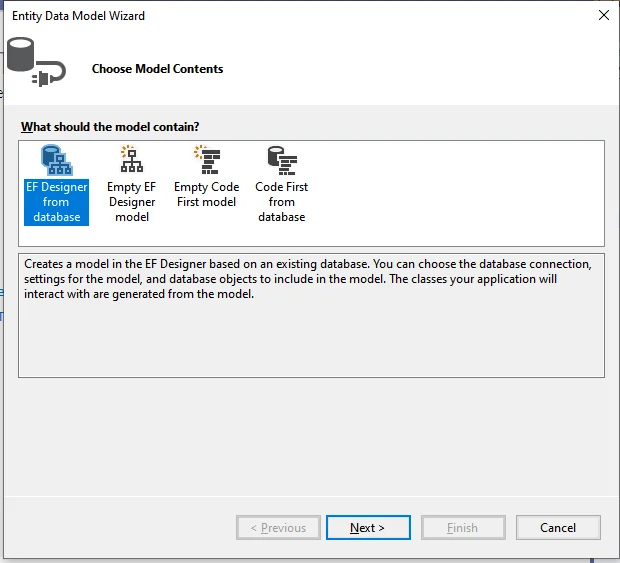
A window will display after clicking on "Next".Select "New Connection.". After that, a new window will open. Enter your server's name, followed by a dot if it's a local server (.). Click "OK" after selecting your database.
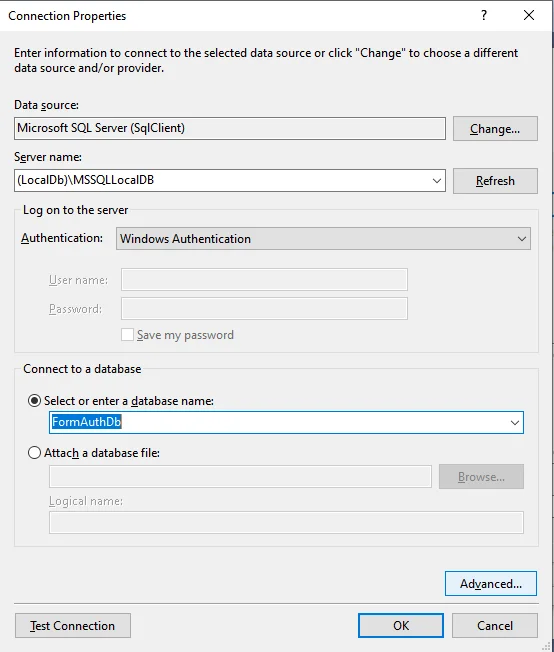
The connection will be established. Save the connection name as you wish. Below is where you can modify the name of your connection. The connection will be saved in the web configuration. Now click on the "Next" button.
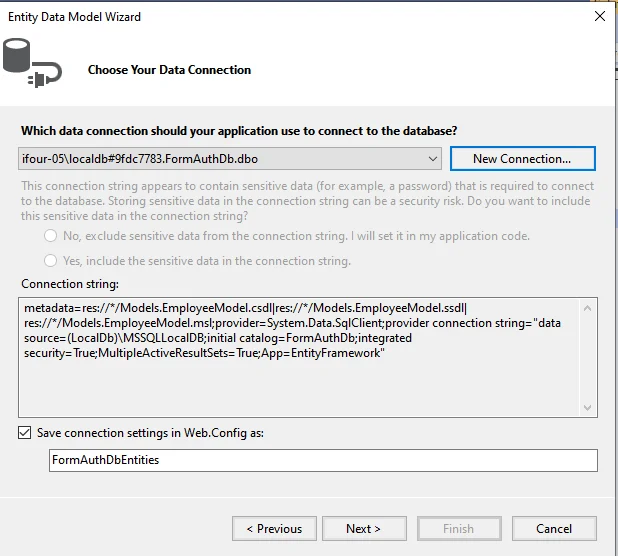
A new window will display after you click NEXT. Click "Finish" after selecting the database table name as seen in the screenshot below.
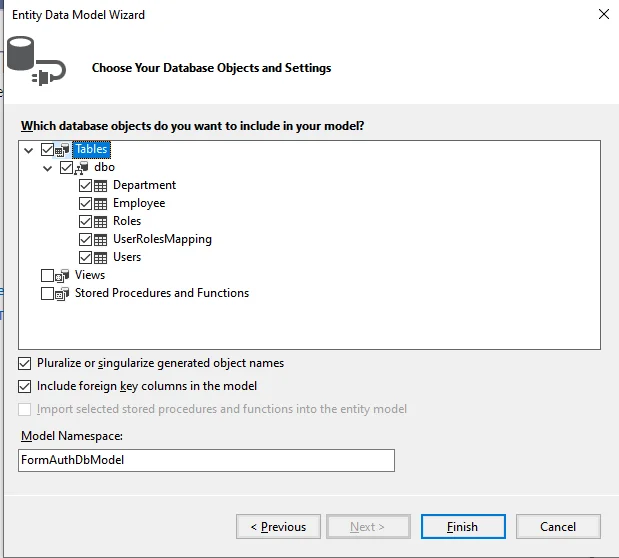
Now, Entity Framework is added, and a class is created for each entity in the Models folder.
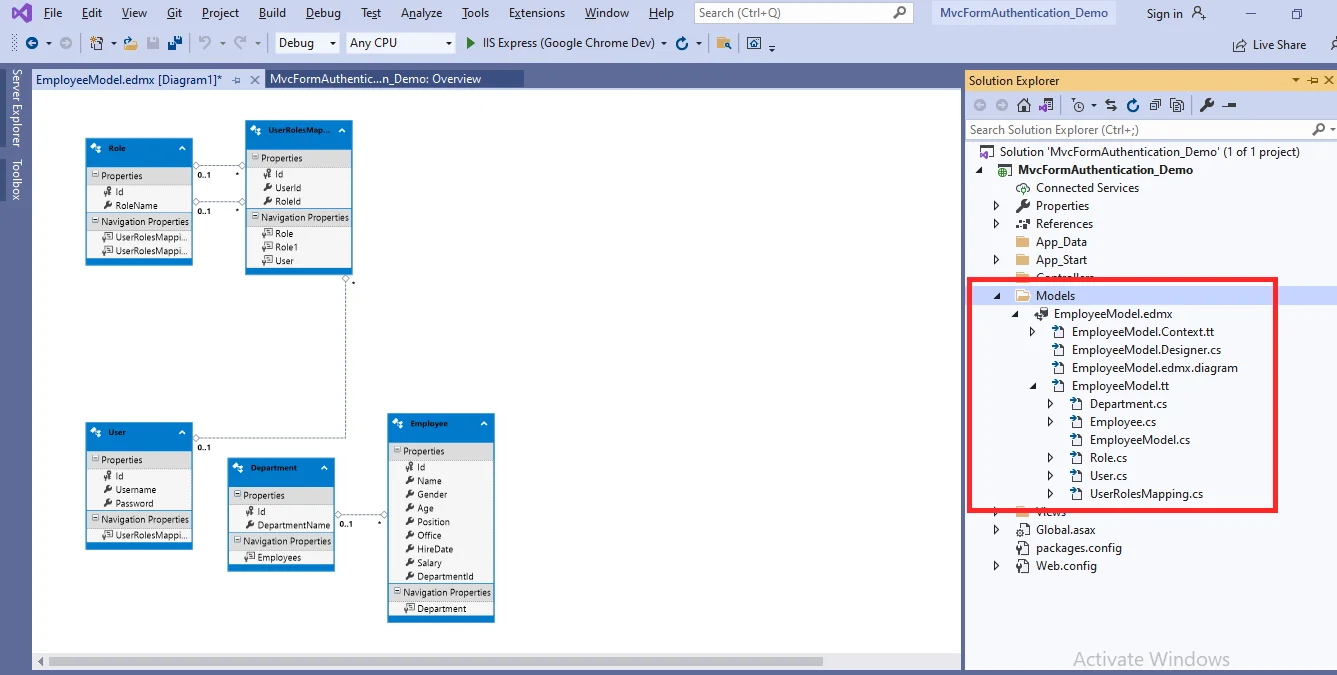
Step 6
Now right-click the Controllers folder and then choose Add Controller.
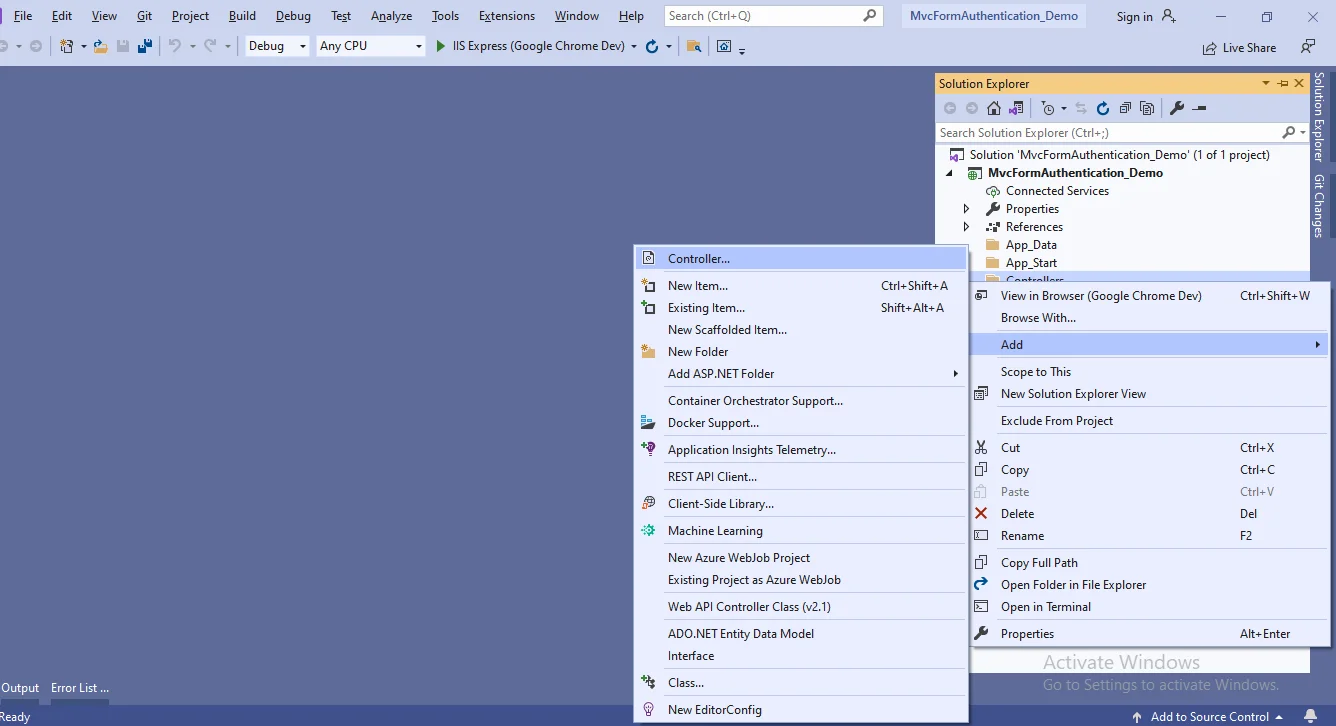
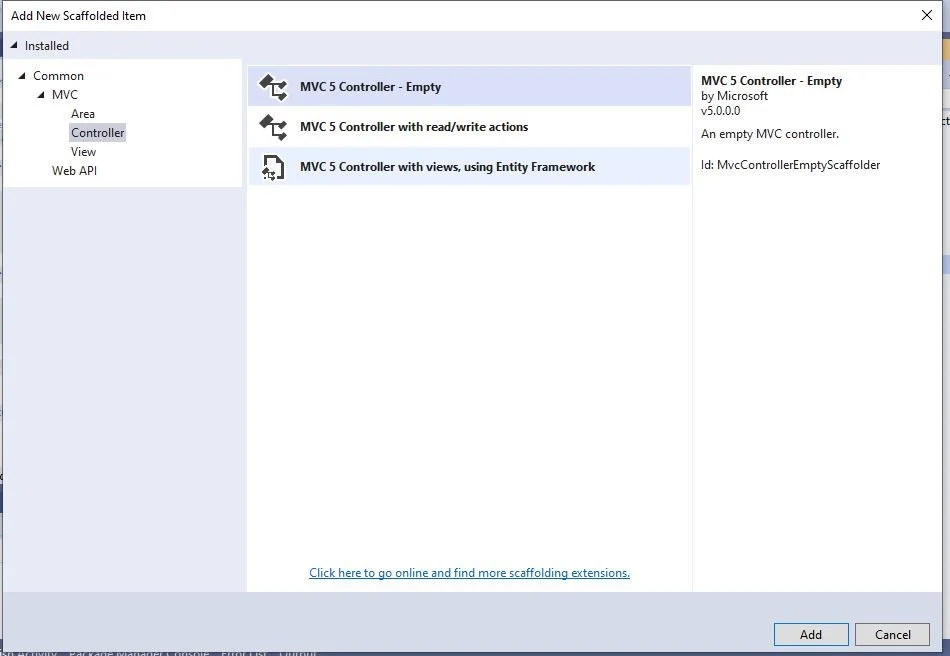
There will be a window appear. Click "Add" after selecting MVC5 Controller-Empty.
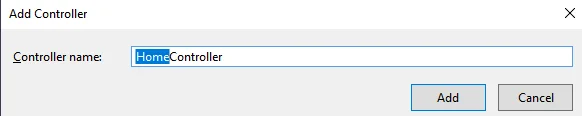
After selecting "Add," a new window with the name DefaultController will appear. Then change the name to the controller HomeController and then click on Add.
Step 7
When you right-click on the Index method in HomeController, the "Add View" dialogue will pop up, with the default index name selected (use a Layout page), and after that select the "Add" button to add a view for the index method.
Complete code for HomeController
Create two views, one for registration and the other for login.
Register View Code
Register View Code
Login View Code
Looking for Trusted Dot Net Development Company For Your Business?
Step 8
Add the following code to the system.web section of the web.config file for forms authentication.
Step 9Similarly, another controller for CRUD operations should be added by right-clicking on the Controllers folder and select Add Controller.
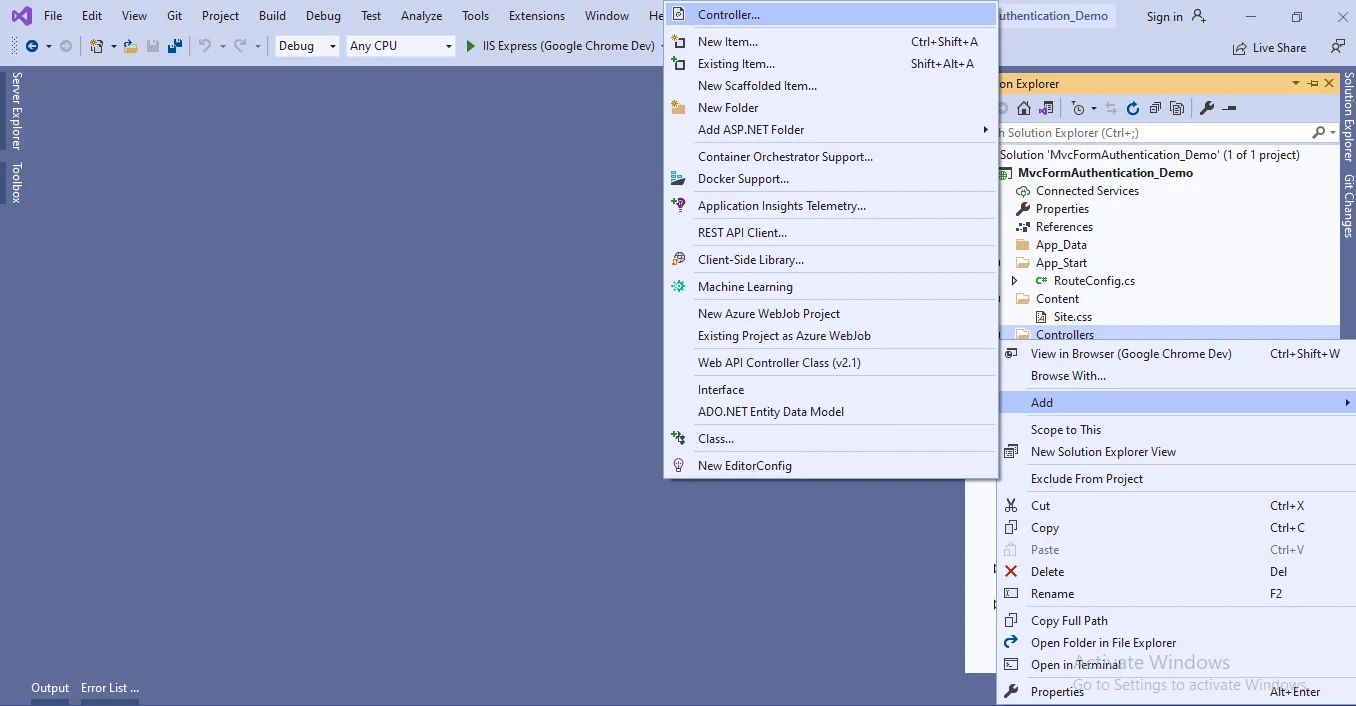
A new window will open. Click "Add" to add an MVC5 Controller with a view that uses Entity Framework.
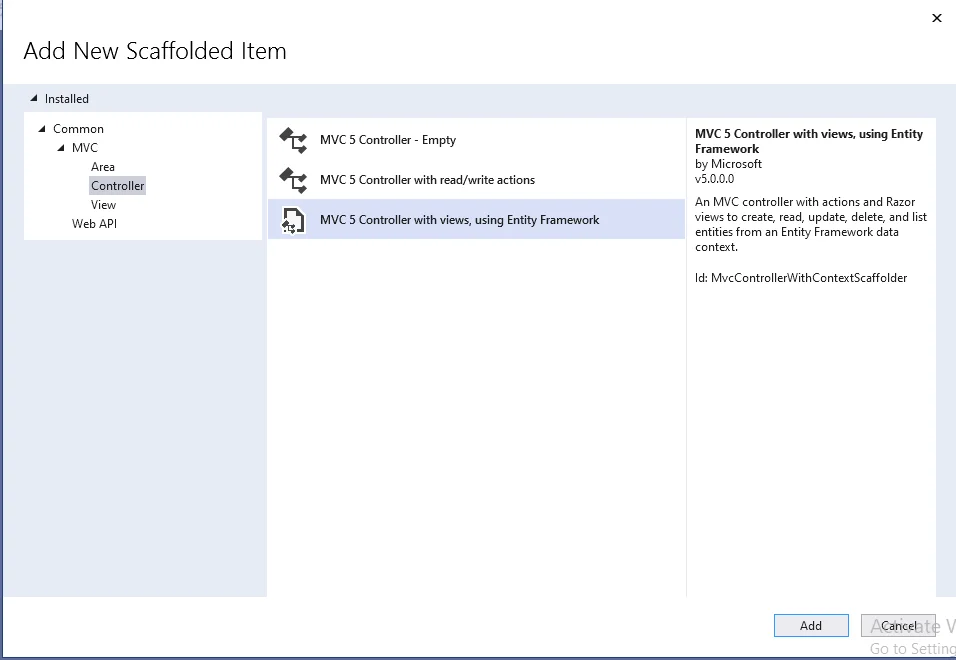
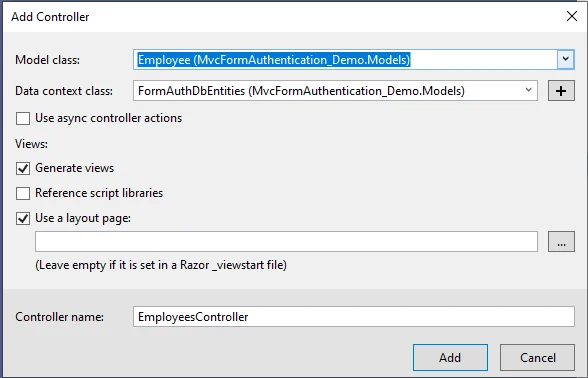
A new window will display after clicking on "Add", Select a model class and a database context class, and then click on Add. It will create the respective views with the controller - create, edit, update, and delete code and views.
Use Authorize Attribute
The Authorize Attribute is a built-in MVC attribute that is used to authenticate a user.Use the Authorize Attribute to protect the action methods that you don't want anonymous users to see.
Step 10
Example
Modify the _Layout.cshtml file with the following code.
Step 11.Build and run your ASP.net web application with ctrl + F5
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned forms authentication in the Asp.Net web application with an example. It will effectively help in comprehending the essentiality of authentication.
Content source: https://www.ifourtechnolab.com/blog/explain-forms-authentication-in-asp-net-mvc



.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment